|
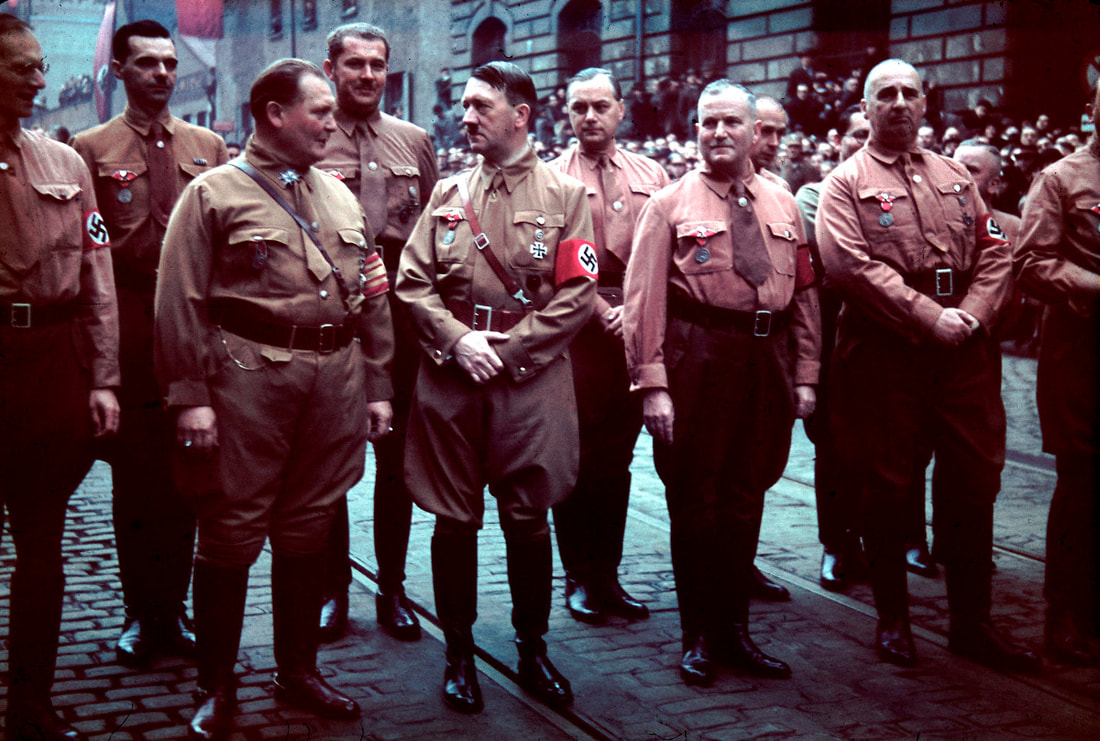
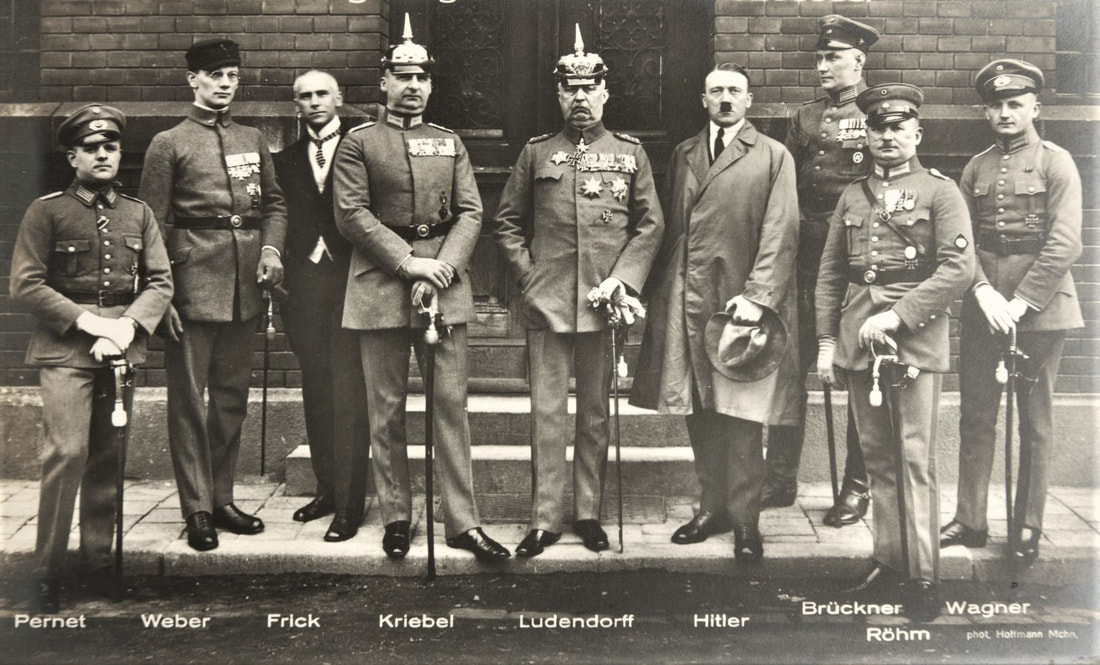
The Munich Putsch The Munich Putsch, also known as the Beer Hall Putsch, was a failed coup attempt by Hitler and his small, provincial Nazi Party in Germany in 1923. It ended in failure, Hitler's arrest and a number of deaths to members of the NSDAP. The Putsch was a significant event in the early history of the Nazi Party and had some far-reaching consequences. In this article, we will examine some of the significant consequences of the Munich Putsch which should be considered when examining this early watershed moment in twentieth century German history and politics. Consequence One: Rise of Adolf Hitler The Munich Putsch was a turning point in the life of Adolf Hitler, who was the leader of the Nazi Party at that time, having shunted aside its founder (and the significantly less charismatic) Anton Drexler. The Putsch provided Hitler with a platform to gain national attention and establish himself as a leader, moving his notoriety beyond its initial Bavarian origins. After the Putsch failed, Hitler was put on trial for high treason, using the courtroom to deliver extended diatribes against the ‘November Criminals’, the Treaty of Versailles, democrats, communists and politicians. Historian Ian Kershaw states, "Hitler's trial for high treason became a vehicle for him to put his views before a wider public, to make a martyr of himself and to build up a myth of personal invincibility." Hitler's trial lasted for several weeks, during which he used the courtroom as a stage to propagate his ideas and beliefs. Hitler's speech during his trial became famous as the "Mein Kampf speech," as it laid the foundation for his book Mein Kampf, which he narrated while he was in prison. The Putsch was a critical moment in the rise of Hitler, as it allowed him to gain national attention and to solidify his ‘man of action’ persona. After his release from prison, havings served a paltry nine months of a five-year sentence, Hitler reorganized the Nazi Party and focused on achieving power through legal means, which ultimately led to his appointment as Chancellor in 1933. Strengthening of the Weimar Republic The Munich Putsch was also significant in strengthening the Weimar Republic, the democratic government of Germany established after World War I. The Putsch was a direct challenge to the authority of the Weimar government, and its failure was a significant blow to the Nazi Party and its supporters. According to historian William L. Shirer, "The Munich Putsch...marked the end of the Nazi Party's first attempt to seize power and demonstrated the strength of the Weimar Republic and its institutions." The Weimar Republic was able to withstand the challenge posed by the Putsch and the subsequent trial, which showed the world (and perhaps more importantly, the German people) that the German government was stable and functioning. The Putsch also led to the banning of the Nazi Party in some parts of Germany, which weakened the Party's influence and curtailed its chances of gaining power through illegal means. The Weimar Republic also took steps to improve its security apparatus and prevent future coup attempts, which made it more resilient to political instability. Polarization of German Politics The Munich Putsch had a significant impact on the political landscape of Germany. The Putsch highlighted the deep divisions within German society and created a polarization between left-wing and right-wing groups. According to historian Richard J. Evans, "The Putsch was a turning point in the development of the Nazi Party...It polarized German politics, dividing the country into two irreconcilable camps, the defenders of the Republic and the enemies of democracy." The failure of the Putsch led to a surge in support for left-wing parties, which were seen as defenders of the Weimar Republic. The Communist Party of Germany (KPD) gained significant support, especially in working-class areas, where it was seen as the main force opposing the Nazi Party. Ironically, those on the extreme left also had a vested interest in diminishing democracy, seeking to facilitate revolutions of their own, notably the Spartacists in 1919. The polarization created by the Putsch in many ways set the stage for the political instability that followed in the years leading up to the Nazi Party's rise to power. The final word ... The Munich Putsch was a critical event in the early history of the Nazi Party and had some far-reaching consequences. The Putsch provided Hitler with a platform to gain national attention and establish himself as a national 'Volkisch' leader, temporarily strengthened the Weimar Republic by demonstrating its resilience, and polarized German politics by creating yet further division between left-wing and right-wing groups. While all three consequences were significant, the rise of Adolf Hitler would have the most significant impact on Germany and the world. The Munich Putsch was a critical moment in the rise of Hitler, as it afforded him national attention and established himself as a national figure, and, in time, the leadership of the broader 'Volkisch' movement. It also inspired him to write Mein Kampf, which laid out his garbled vision for a Nazi-dominated Germany and Europe. Ultimately, Hitler learned that the process of ‘Putsch’ would be fruitless and that he needed to adopt a pragmatic - and ultimately political - pathway to power. Written by Versus History guest contributor Alexa Mowbray.
0 Comments
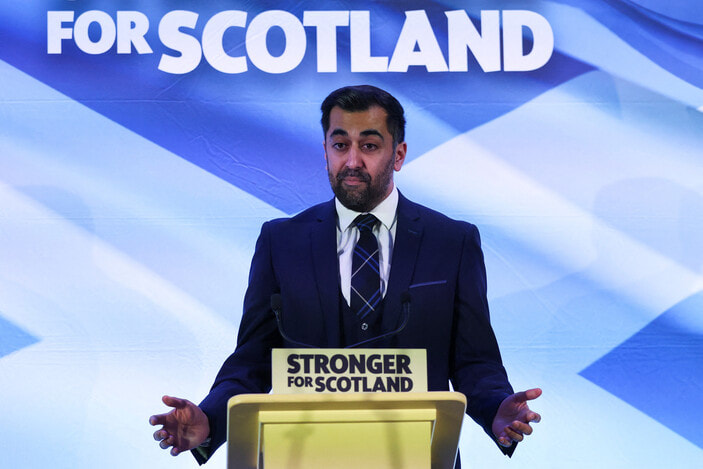
On 27 March 2023, the Scottish National Party (SNP) elected Humza Yousaf as its new leader, polling a Brexit-esq '52%' of the members vote, taking over from former First Minister Nicola Sturgeon. Needless to say, 52% of the vote means that he didn't achieve 48% of it, so he has some serious work to do to bring about consensus and party unity within the SNP, which will be no easy task. Given the extended length of the SNP's tenure government, he may not benefit from a transitionary 'honeymoon period' to acclimatise to the demands of the role, either. Yousaf has a range of policy options to choose from as he sets out his vision for the future of Scotland. In this article, we will outline five potential policy options that he might focus on, and examine the evidence and statistics that support them. 1. Scottish Independence No surprises here. One of the key issues that Yousaf is likely to focus on is Scottish independence. It is the raison d'être of the SNP, after all. The SNP has long campaigned for Scotland to become an independent country, separate from the rest of the United Kingdom. The most recent poll on the issue found that 47% of Scottish voters supported independence, while 45% were against it. This suggests that there is still a significant amount of support for independence in Scotland, and Yousaf may seek to capitalize on this. However, there are significant challenges to achieving independence. Firstly, the UK government has consistently stated that it will not grant permission for a second independence referendum, which would be required for Scotland to become independent. Additionally, the economic consequences of independence are uncertain, with some experts suggesting that Scotland would face significant challenges in establishing itself as an independent nation. 2. Climate Change Yousaf has spoken extensively about the need to tackle climate change, and this is likely to be a key policy focus for him. Scotland has set ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, with a goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2045. The country is currently on track to meet this target, with emissions falling by 49% between 1990 and 2018. There is still much more work to be done. The Scottish government has committed to investing £1.6 billion in low-carbon infrastructure over the next five years, but some experts argue that this investment needs to be significantly increased if Scotland is to achieve its climate goals. 3. Education Yousaf may also choose to focus on education policy, with the aim of improving outcomes for Scottish students. Scotland has a highly regarded education system, but there are concerns that standards have slipped in recent years. The most recent PISA results, which measure student performance in reading, maths, and science, showed a decline in Scotland's scores compared to previous years. To address this, Yousaf may look to invest in teacher training and support, increase funding for schools, and implement policies to improve student wellbeing. 4. Social Justice Another potential policy focus for Yousaf is social justice. Scotland has a relatively high level of income inequality, with the top 10% of earners receiving 27% of all income. Additionally, there are significant disparities in health outcomes between different socioeconomic groups. To address these issues, Yousaf may look to implement policies such as increasing the minimum wage, increasing funding for public services, and improving access to healthcare for disadvantaged groups. Funding an increase in spending will certainly not be easy in the present economic climate, however ... 5. Immigration Finally, Yousaf may choose to focus on immigration policy, with the aim of making Scotland a more welcoming and inclusive society. Scotland has a relatively low level of immigration compared to other parts of the UK, and some experts argue that this has contributed to the country's demographic challenges, such as an ageing population and a declining workforce. Yousaf may look to implement policies to attract more immigrants to Scotland, such as offering incentives for skilled workers to relocate to the country, and increasing support for refugees and asylum seekers. The final word ...
In conclusion, Humza Yousaf has a range of policy options to choose from as he sets out his vision for the future of Scotland. Scottish independence, climate change, education, social justice, and immigration are all potential areas of focus. While each of these policy options has its challenges, there is also evidence to suggest that they could be successful in improving outcomes for the people of Scotland. Yousaf will need to carefully consider the evidence and statistics surrounding each policy option, and work to build consensus (which will not easy, given the 'broad church' nature of the SNP) around his chosen priorities. It is worth noting that Yousaf will face significant challenges in implementing his policies, particularly given the current political landscape in Scotland and the wider UK. However, his position as leader of the SNP gives him a significant platform from which to advocate for change, and he will possibly be able to shape the political agenda in Scotland for years to come. Ultimately, the success of Yousaf's policies will depend on a range of factors, including political support, public opinion, and economic conditions. However, by focusing on issues such as climate change, education, social justice, and immigration, Yousaf has the potential to make a significant and positive impact on the lives of people in Scotland. Contributed by Versus History's guest current & historical affairs blogger 'JHZ' Tweet us @versushistory to discuss this or any other aspect of History. |
Categories
All
Archives
April 2024
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed